Companies operating online try various ways to defend themselves against illegal access to their client’s data. Even a solid password, created following the guidelines required by network administrators, may not be the best weapon against online thieves. Then, multi-factor authentication, including SMS verification, may become the right choice to avoid data leakages.
Data that can be captured while using the internet can lead not only to the loss of accounts on social networks. Worse things happen when the target of thieves is a bank account or sensitive company data. This situation forces companies to implement tools to authenticate the login process in their systems.
Single-factor Verification
A one-factor method is the most popular way to protect your data and accounts with two simple pieces of information: log in and a password. Another form of unified authentication is biometrics, i.e. fingerprints. This time we will focus on the more complicated way – multi-factor authentication (so-called MFA).
Multi-factor Authentication
The multi-factor authentication (MFA) method involves using at least three elements: something you are (inherence factor), something that you possess (possession factor), something you know (knowledge factor).
It is possible to use 2, 3, 4 and even 5-elements of authentication. Access to important data requires a minimum of three factors, the diversity of which is shown in the following illustration:
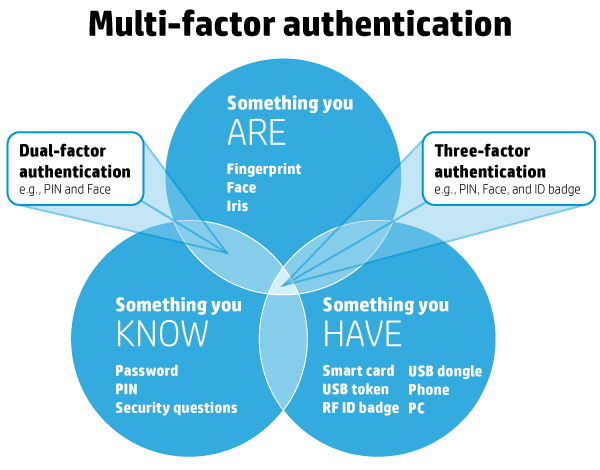
Source: https://dev98.de/2016/11/19/a-multi-factor-authentication-quickstart
1. Something you know
It can be a typical password or pin that should be entered in the appropriate window. The level of security of this kind of factor depends on the length and complexity (use of different types of alphanumeric characters- both 1,2,3 and XYZ).
It is also important to protect and preserve access to your passwords (it is also good not to write them on yellow cards on the monitor).
2. Something you are
Identifying faces or reading fingerprints is not yet widely used and has already been partially questioned as an effective security method. It turns out that even the fingerprint can be faked, just like you can trick FaceID with a face mask.
3. Something you have
It can be a FlashDrive plugged into a computer, a door opening card or other items that will allow you to authorize your access. But! At the same time, it is going to work with the phone in your pocket! Using the last solution, the user has to pass particular stages and in the end, receives a code via SMS.
In comparison with other methods, this one is easy to implement as mobile banks and tech companies have been using such solutions for a long time. What is also important, choosing this factor ensures that the device will always be close to the user (in his/her pocket/bag).
How to plan data protection?
Current technology development allows us to implement a security system worthy of the White House, but we should always remember its usability. The authentication method has to be adapted to the type of protected data and the level of their secrecy. Every regular user will be upset if you force him to go through a 5-steps control so that he can check e-mail.
On the other hand, along with the development of technology, the possibilities of digital robbers also grow. Therefore it is worth taking into account the dangers of hiding in the network, properly secure yourself, but in a useful and intuitive way for the client. From this, among others, the popularity of text messages with code follows.
We recently surveyed Americans across the US and discovered that nearly 58% have experienced a data breach because of poor password security. More alarming is that despite the fact that over 21% had their financial accounts hacked, people don’t seem convinced in the importance of good password habits, including using different, strong passwords for every account. Because of this, our team of researchers have created a series of resources and tools to help internet users keep their passwords safe – an essential defence to fight against scams, fraud, and identity theft.
Source: Password Manager
SMSAPI introduces SMS Authenticator
Regarding the data protection needs, we have prepared a service that will confirm the user’s identity with an SMS code sent automatically to his/her mobile phone (using the factor “Something that you have” – so-called SMS Verification). You have to enter the number to be checked, and SMSAPI will send the security code and check if it is correct.
SMS Authenticator
If you want to know more details about the brand new SMS verification feature – go here!
The weakest authentication aspect is…
When the login procedure is built of several elements, the certainty that any unauthorized person will be able to get possession of the protected data is almost one hundred per cent.
Almost because there is always one weakest link, regardless of method – a user who can inadvertently leave behind traces, bringing digital thieves to the data they are looking for. It is worth making their operation as difficult as possible, expanding your defence with multi-factor authentication.





